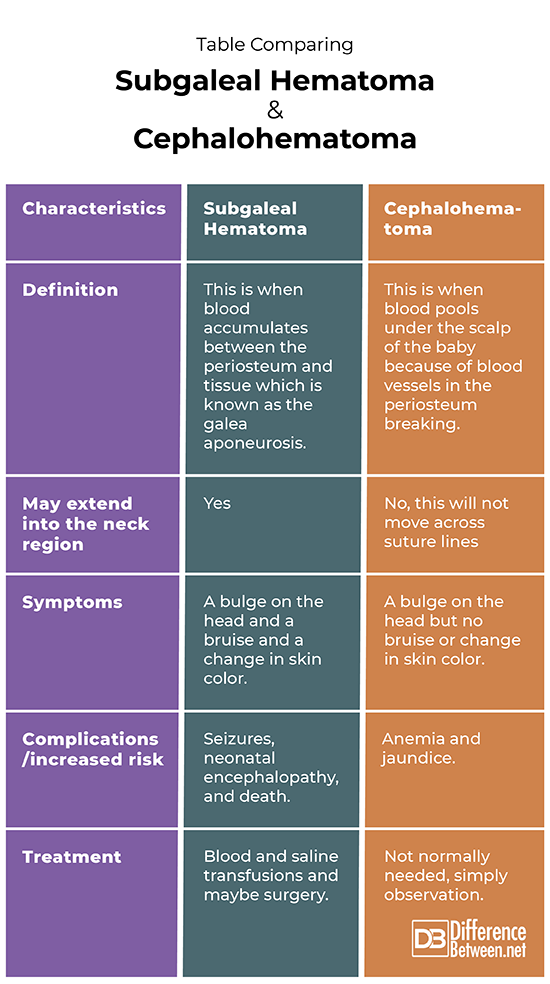
Subgaleal complications are a critical concern in medical science, particularly in the context of neonatal care and cranial anatomy. The subgaleal space plays a significant role in understanding various health conditions, especially those related to head injuries and surgical procedures. This article aims to provide an in-depth exploration of subgaleal anatomy, its clinical implications, and management strategies. Whether you're a medical professional, student, or simply someone seeking knowledge, this guide offers valuable insights into the complexities of subgaleal issues.
The term "subgaleal" refers to the anatomical space beneath the galea aponeurotica, a dense fibrous layer covering the skull. This area is crucial in medical practice due to its proximity to vital structures and the potential for complications. Understanding the subgaleal space is essential for diagnosing and treating conditions that may arise in this region.
As we delve into this topic, we will explore the anatomy, causes of subgaleal complications, diagnostic methods, treatment options, and preventive measures. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of the significance of the subgaleal space and its relevance in medical practice.
Read also:Kiki Klout Unveiling The Rising Star In The Entertainment Industry
Table of Contents
- Anatomy of the Subgaleal Space
- Causes of Subgaleal Hemorrhage
- Symptoms and Clinical Manifestations
- Diagnosis of Subgaleal Conditions
- Management and Treatment Options
- Role of Surgery in Subgaleal Issues
- Preventive Measures for Subgaleal Complications
- Statistics and Research Findings
- Case Studies and Real-Life Examples
- Future Research Directions
Anatomy of the Subgaleal Space
The subgaleal space is an anatomical region located beneath the galea aponeurotica, a tough fibrous layer that connects the frontalis and occipitalis muscles. This space extends from the eyebrows to the occipital region and plays a critical role in various medical conditions. The subgaleal space is relatively loose and contains fat and connective tissue, making it susceptible to fluid accumulation and bleeding.
Key Features of the Subgaleal Space
- Located beneath the galea aponeurotica
- Extends from the eyebrows to the occipital region
- Contains fat and connective tissue
- Prone to fluid accumulation and bleeding
Understanding the anatomy of the subgaleal space is crucial for diagnosing and treating conditions such as subgaleal hemorrhage, which can be life-threatening if not managed promptly.
Causes of Subgaleal Hemorrhage
Subgaleal hemorrhage is a serious medical condition that occurs when there is bleeding into the subgaleal space. This condition is most commonly associated with birth trauma, particularly during vacuum-assisted deliveries. Other potential causes include:
Common Causes of Subgaleal Hemorrhage
- Vacuum-assisted delivery
- Forceps delivery
- Preterm birth
- Coagulation disorders
- Trauma to the head
Early recognition of the causes of subgaleal hemorrhage is vital for effective management and prevention of complications.
Symptoms and Clinical Manifestations
The symptoms of subgaleal hemorrhage can vary depending on the severity and extent of bleeding. Common symptoms include:
- Swelling of the scalp
- Pallor
- Rapid heart rate
- Decreased blood pressure
- Difficulty breathing
In severe cases, subgaleal hemorrhage can lead to significant blood loss and shock, necessitating immediate medical intervention.
Read also:Is Christian Kane Married Discover The Truth Behind The Actors Relationship Status
Diagnosis of Subgaleal Conditions
Diagnosing subgaleal conditions requires a combination of clinical assessment, imaging studies, and laboratory tests. Physicians often rely on the following diagnostic tools:
Diagnostic Methods
- Clinical examination
- Ultrasound imaging
- CT scans
- MRI
- Complete blood count (CBC)
Early and accurate diagnosis is critical for successful treatment and management of subgaleal complications.
Management and Treatment Options
The management of subgaleal conditions depends on the severity of the condition and the underlying cause. Treatment options may include:
Treatment Strategies
- Fluid resuscitation
- Blood transfusions
- Medications to control bleeding
- Surgical intervention if necessary
In mild cases, conservative management may suffice, while severe cases may require intensive care and surgical intervention.
Role of Surgery in Subgaleal Issues
In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to manage subgaleal complications. Surgery is typically reserved for severe cases where there is significant bleeding or fluid accumulation that cannot be managed conservatively. Procedures may include:
Surgical Procedures
- Drainage of subgaleal hematoma
- Repair of damaged blood vessels
- Management of coagulation disorders
Surgical intervention should always be performed by experienced medical professionals to ensure optimal outcomes.
Preventive Measures for Subgaleal Complications
Preventing subgaleal complications involves a combination of prenatal care, careful delivery techniques, and monitoring for risk factors. Key preventive measures include:
Preventive Strategies
- Prenatal screening for coagulation disorders
- Minimizing the use of vacuum or forceps during delivery
- Monitoring for signs of trauma during delivery
- Education for healthcare providers
Implementing these preventive measures can significantly reduce the incidence of subgaleal complications.
Statistics and Research Findings
Research indicates that subgaleal hemorrhage is a relatively rare but serious complication, occurring in approximately 1 in 2000 deliveries. Studies have shown that vacuum-assisted deliveries increase the risk of subgaleal hemorrhage by up to 10 times compared to spontaneous vaginal deliveries. Early recognition and management are critical for improving outcomes.
National Institutes of Health and World Health Organization provide valuable resources for further research and understanding of subgaleal conditions.
Case Studies and Real-Life Examples
Several case studies highlight the importance of early diagnosis and treatment of subgaleal complications. For example, a case study published in the New England Journal of Medicine described a neonate who developed subgaleal hemorrhage following vacuum-assisted delivery. Prompt recognition and management led to a successful outcome.
These real-life examples underscore the significance of education and training for healthcare providers in managing subgaleal conditions.
Future Research Directions
Further research is needed to explore the underlying mechanisms of subgaleal complications and develop more effective prevention and treatment strategies. Areas of interest include:
Potential Research Topics
- Genetic factors influencing coagulation disorders
- Development of less invasive delivery techniques
- Improving diagnostic tools for early detection
- Evaluating the long-term effects of subgaleal hemorrhage
Advancements in research will undoubtedly lead to better outcomes for patients affected by subgaleal complications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the subgaleal space and its associated complications is essential for medical professionals and anyone interested in cranial anatomy. This article has explored the anatomy, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and management of subgaleal conditions, providing a comprehensive overview of this critical topic.
We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences in the comments section below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our website for further insights into medical science and healthcare. Together, we can promote awareness and improve outcomes for those affected by subgaleal complications.